Guide to Passive Electronic Components
Introduction
Electronic components are essential elements in electronic circuits that do not require external power to operate. They function to resist, store, and transfer energy. This guide provides an overview of common passive components, including resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, and their applications.
Resistors
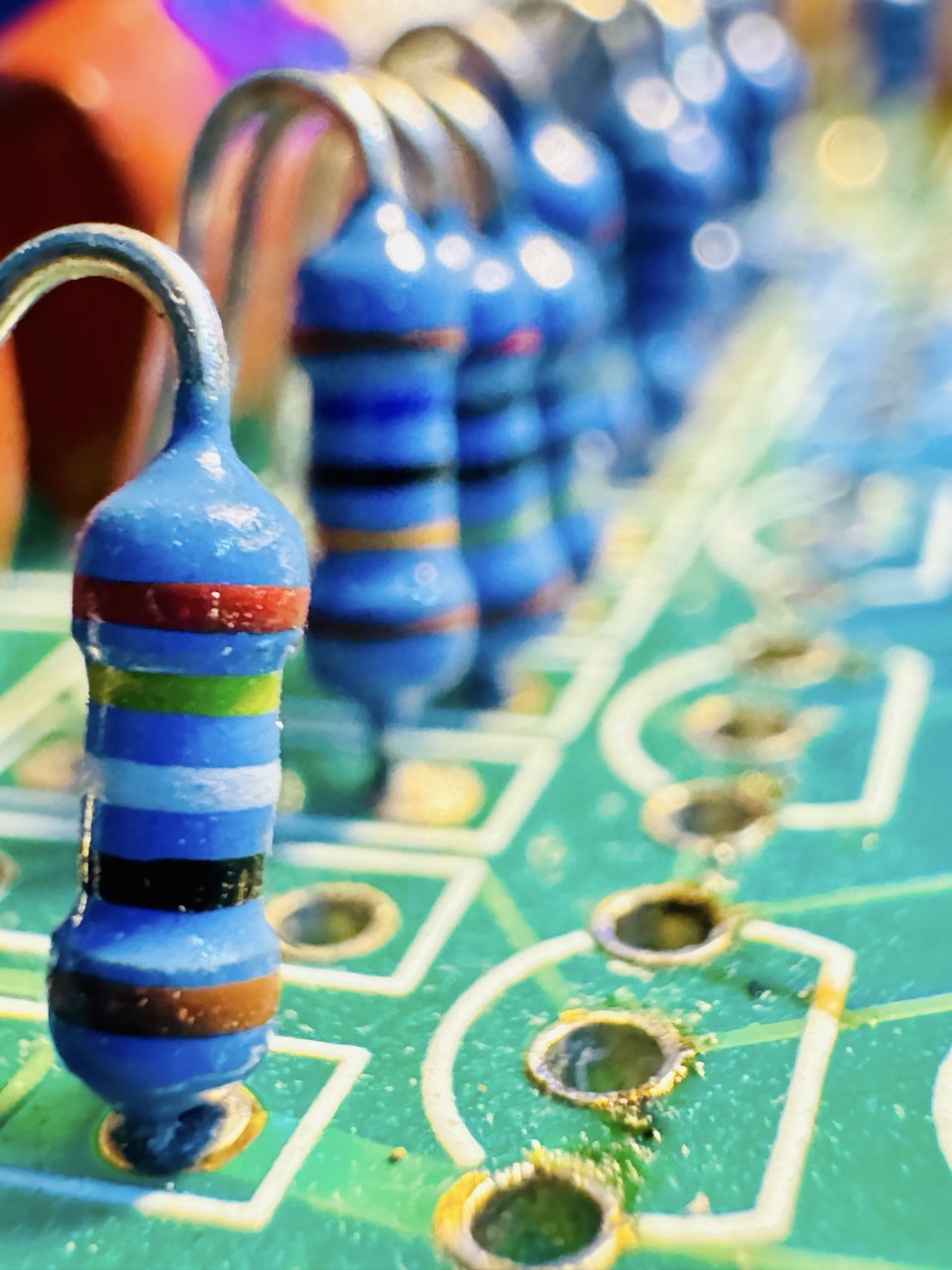

Description: Small cylindrical components with color-coded bands, designed to limit current flow.
Measurement: Resistance is measured in ohms (Ω).
Types of Resistors
Fixed Resistors: Deliver a constant resistance value. Common subtypes include carbon film (cost-effective) and metal film (high precision).
Example: Used in LED circuits to limit current and prevent burnout.
Variable Resistors (Potentiometers): Allow manual resistance adjustment via a knob or slider.
Example: Adjusting volume on a stereo or tuning a radio.
Thermistors: Temperature-sensitive resistors; NTC (negative temperature coefficient) decreases resistance as temperature rises, while PTC (positive temperature coefficient) increases it.
Example: NTC thermistors in thermostats; PTC in overcurrent protection.
Photoresistors (LDRs - Light-Dependent Resistors): Resistance drops with increased light exposure.
Example: Streetlights that activate at dusk.
Applications
Resistors are used in circuits to control voltage, limit current, divide voltage, and protect sensitive components.
Capacitors
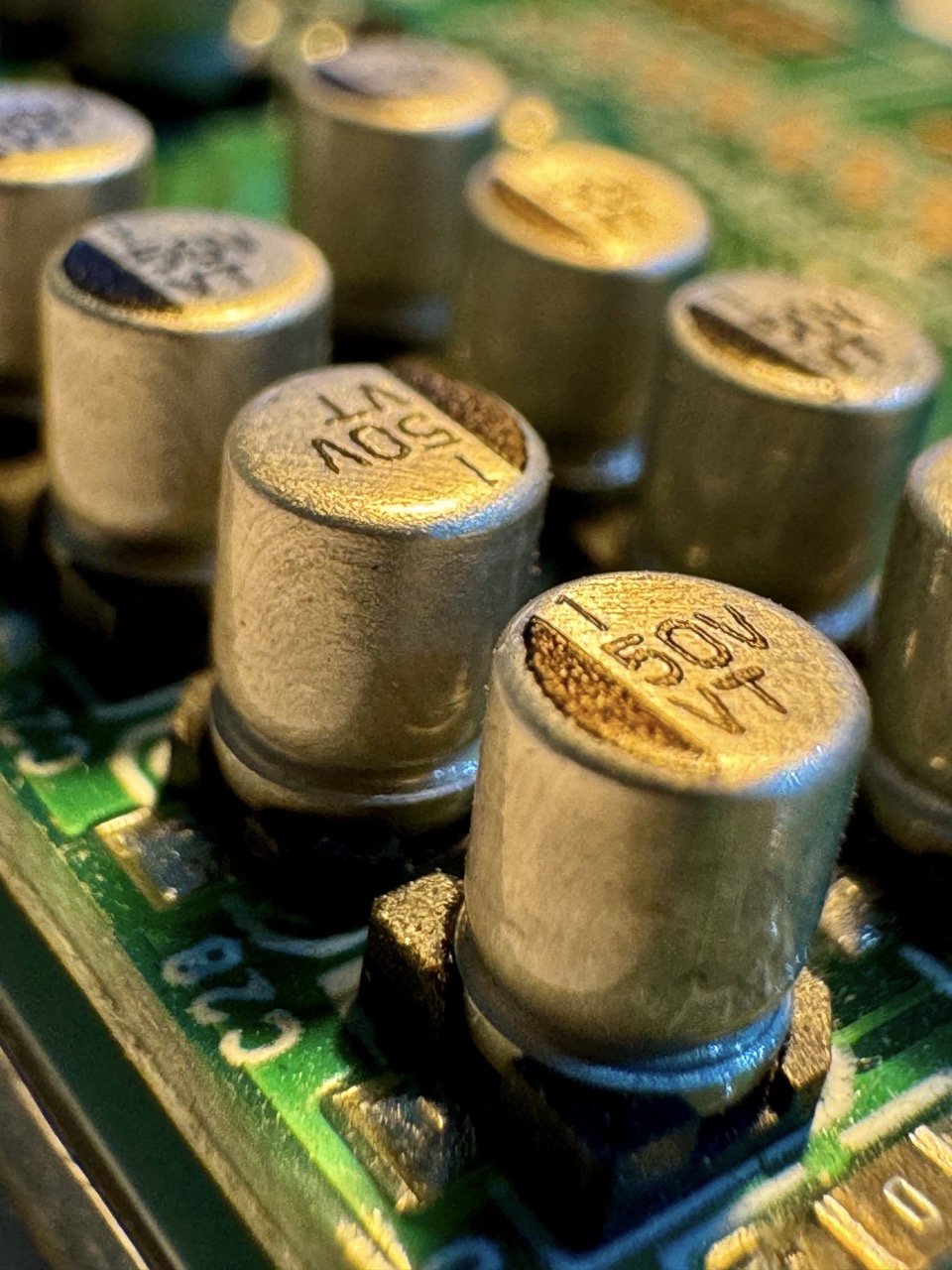
Description: Cylindrical or rectangular components with two leads, used to store and release electrical energy.
Measurement: Capacitance is measured in farads (F).
Types
- Ceramic Capacitors: For high-frequency applications.
- Electrolytic Capacitors: High capacitance, used for power supply filtering.
- Film Capacitors: Stable and accurate for low-frequency circuits.
Applications
- Power supply filtering
- Signal coupling/decoupling
- Flash circuit energy storage
Additional Resource
Learn how to choose the right capacitor for your project: Selecting the Right Capacitor
Inductors
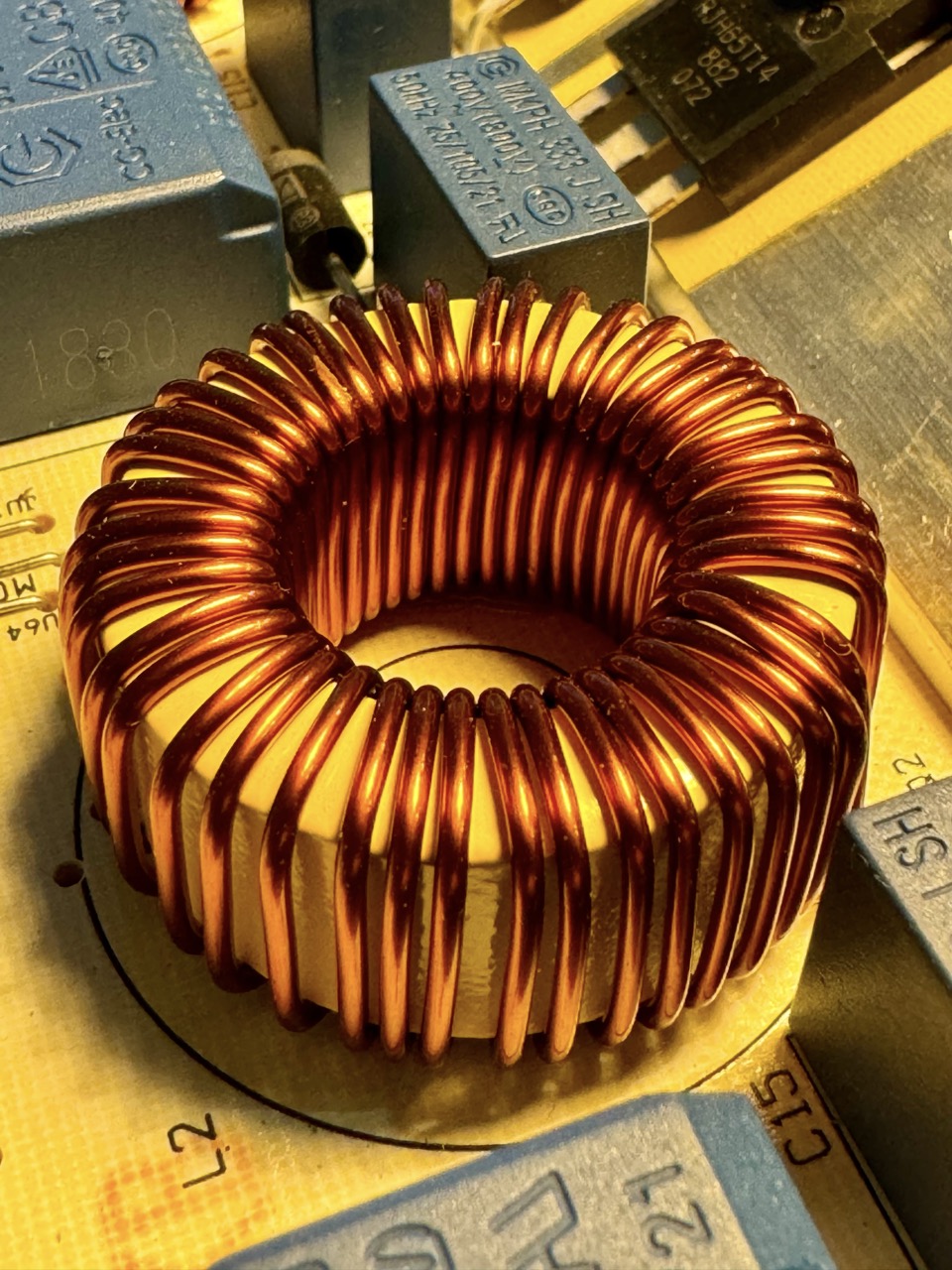
Description: Coil-shaped components that store energy in a magnetic field.
Measurement: Inductance is measured in henries (H).
Types
- Air Core Inductors: High-frequency applications.
- Ferrite Core Inductors: Low-frequency applications.
- Toroidal Inductors: Efficient magnetic field containment.
Applications
- Power supply filtering
- RF tuning
- Choke coils in electronics
Diodes
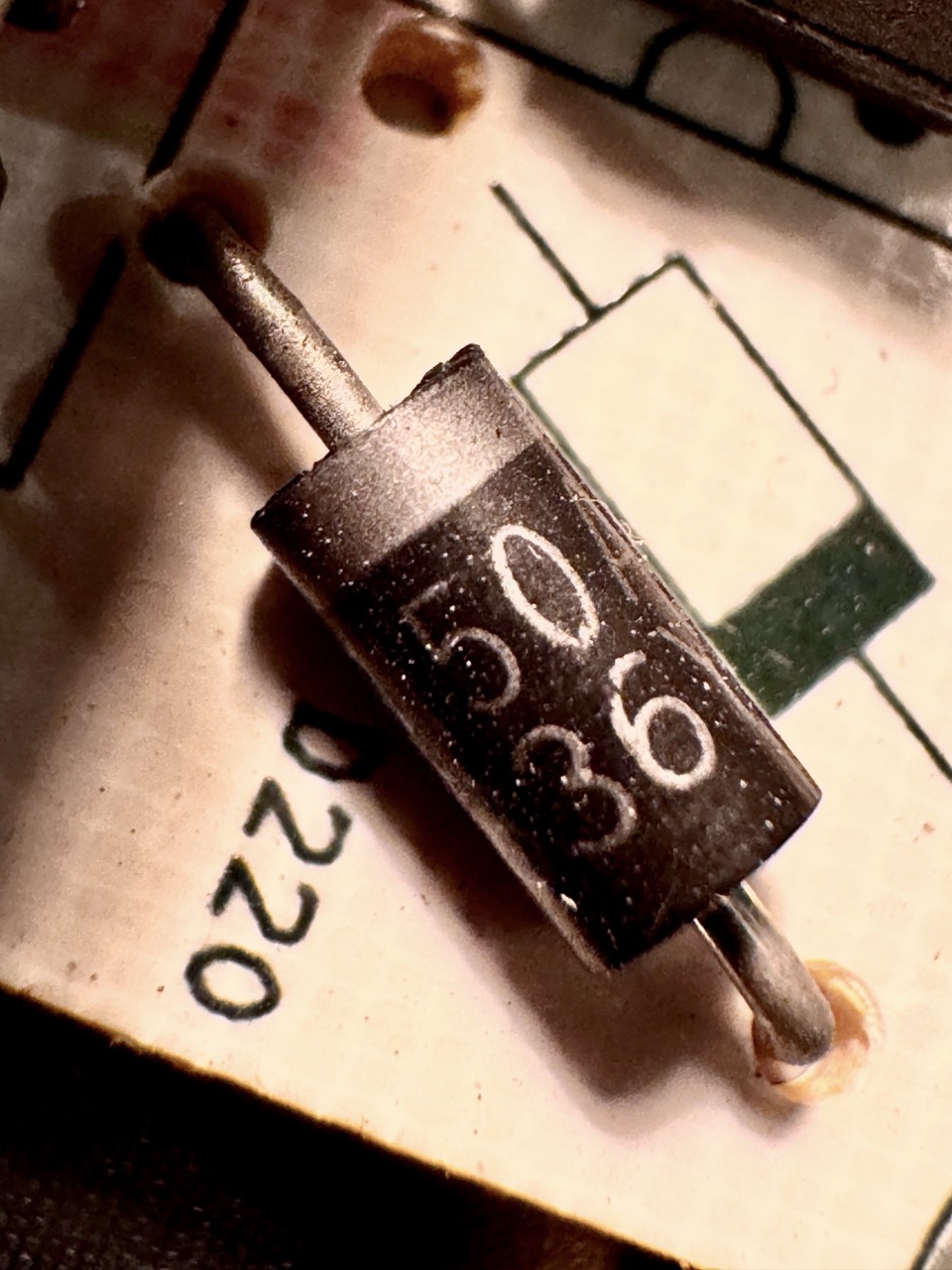
Description: Allows current flow in one direction only, protecting circuits from reverse polarity.
Types
- Rectifier Diodes: Convert AC to DC.
- Zener Diodes: Voltage regulation.
- LEDs: Emit light when current flows through.
Applications
Varistors

Varistors are voltage-dependent resistors that provide protection against voltage spikes. When the voltage exceeds a certain threshold, the resistance of the varistor decreases, allowing current to bypass sensitive components.
Applications
Transformers
Description: Devices with coils wound around a core, transferring energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction.
Types
- Step-Up Transformers: Increase voltage.
- Step-Down Transformers: Decrease voltage.
- Isolation Transformers: Provide circuit isolation.
Applications
- Power distribution
- Voltage regulation
- Electrical isolation
Fuses
Description: Break the circuit when current exceeds a limit, protecting devices from damage.
Types
- Slow-Blow Fuses: Allow short current bursts.
- Fast-Acting Fuses: Blow quickly to protect sensitive components.
Applications
- Power supply protection
- Household appliance safety
Conclusion
Passive components are foundational to electronic circuits, performing vital roles like energy storage, filtering, and protection. Understanding these components enhances the reliability and functionality of circuit designs, from simple projects to complex systems.
For more hands-on experience, consider starting with an ESP32 Electronics Starter Kit or an Arduino Starter Kit for experimenting and prototyping.
For more details, explore datasheets, online resources, or component-specific tutorials. To gain a complete understanding, also consider reviewing our Active Components tutorial, which covers components like transistors, LEDs, and diodes that amplify or switch electrical signals.
If you're new to electronics, check out our Introduction to Measuring guide. This page explains essential measurement techniques using tools like multimeters and oscilloscopes, which are crucial for troubleshooting and testing circuits.
Want to dive deeper? Explore this Free book on electronics at Amazon that covers fundamental concepts with descriptions of everyday applications, engaging illustrations, and interactive lessons.
And finally, explore "100 Passive Experiments" for ideas to practice your skills with passive components and simple circuits!
100 Passive Components Experiments
- 1. LED Current Limiting Resistor Experiment
- 2. Resistor Voltage Divider Experiment
- 3. Inductor in a DC Circuit Experiment
- 4. Diode Rectification Experiment
- 5. Zener Diode Voltage Regulation Experiment
- 6. Ferrite Bead Noise Suppression Experiment
- 7. Varistor Overvoltage Protection Experiment
- 8. NTC Thermistor Temperature Sensing Experiment
- 9. PTC Thermistor Overcurrent Protection Experiment
- 10. Quartz Crystal Oscillator Frequency Stability Experiment
- 11. Ceramic Resonator Signal Generation Experiment
- 12. Coupling Capacitor Signal Transmission Experiment
- 13. Bypass Capacitor Power Filtering Experiment
- 14. Trimmer Resistor Circuit Tuning Experiment
- 15. Surface Mount Resistor Usage Experiment
- 16. Film Capacitor in AC Circuits Experiment
- 17. Electrolytic Capacitor Energy Storage Experiment
- 18. Tantalum Capacitor Ripple Filtering Experiment
- 19. Supercapacitor Energy Backup Experiment
- 20. Polymer Capacitor Efficiency Experiment
- 21. Air-Core Inductor Electromagnetic Induction Experiment
- 22. Iron-Core Inductor in Power Circuits Experiment
- 23. Planar Inductor in RF Circuits Experiment
- 24. Toroidal Inductor in Filters Experiment
- 25. Transformer Voltage Conversion Experiment
- 26. RF Choke High-Frequency Filtering Experiment
- 27. Balun Transformer Signal Balancing Experiment
- 28. Surface Acoustic Wave (SAW) Filter Experiment
- 29. Band-Pass Filter Design Experiment
- 30. Low-Pass Filter for Audio Circuits Experiment
- 31. High-Pass Filter for Signal Transmission Experiment
- 32. Notch Filter for Noise Reduction Experiment
- 33. Pi Filter in Power Supply Experiment
- 34. T-Filter for Signal Conditioning Experiment
- 35. LC Filter for RF Applications Experiment
- 36. EMI Filter in Power Circuits Experiment
- 37. RC Filter Signal Smoothing Experiment
- 38. LC Tank Circuit Resonance Experiment
- 39. Delay Line in Signal Transmission Experiment
- 40. RC Snubber Circuit Experiment
- 41. Split-Core Current Transformer Experiment
- 42. Current-Sense Resistor Experiment
- 43. Shunt Resistor in Power Measurement Experiment
- 44. Precision Resistor Circuit Accuracy Experiment
- 45. LDR Light Sensing Experiment
- 46. VDR Voltage Protection Experiment
- 47. Capacitive Voltage Divider Experiment
- 48. Resistive Voltage Divider Experiment
- 49. Impedance Matching Transformer Experiment
- 50. Balancing Resistor in Battery Circuits Experiment
- 51. Phase-Shift Capacitor in Power Circuits Experiment
- 52. Energy Storage Capacitor Experiment
- 53. Power Film Capacitor in High-Power Circuits Experiment
- 54. Power Line Filter for EMI Reduction Experiment
- 55. Decoupling Capacitor for Noise Suppression Experiment
- 56. Magnetic Core in Inductor Design Experiment
- 57. Magnetic Loop Antenna Experiment
- 58. Stub Tuner for Impedance Matching Experiment
- 59. Resonant Circuit Design Experiment
- 60. Load Resistor in Power Dissipation Experiment
- 61. TCXO Frequency Stability Experiment
- 62. OCXO Temperature Compensation Experiment
- 63. Power Inductor in Buck Converter Experiment
- 64. Supercapacitor for Energy Storage Experiment
- 65. Coaxial Transformer in RF Experiment
- 66. Inductive Proximity Sensor Experiment
- 67. Piezoelectric Sensor in Vibration Sensing Experiment
- 68. Piezoelectric Buzzer in Sound Generation Experiment
- 69. Ceramic Filter for RF Experiment
- 70. SAW Resonator in Oscillator Experiment
- 71. MEMS Sensor in Accelerometer Experiment
- 72. Bridge Rectifier in Power Conversion Experiment
- 73. Bias Tee for Signal Injection Experiment
- 74. Impedance Matching Network Design Experiment
- 75. Reactive Load in Power Dissipation Experiment
- 76. Polyfuse Resettable Overcurrent Protection Experiment
- 77. MOV in Surge Protection Experiment
- 78. Wire-Wound Resistor for High Power Dissipation Experiment
- 79. Carbon Film Resistor in Low-Power Circuits Experiment
- 80. Thin-Film Resistor in Precision Circuits Experiment
- 81. Thick-Film Resistor in High Voltage Experiment
- 82. Power Resistor Heat Dissipation Experiment
- 83. Precision Capacitor in Timing Circuit Experiment
- 84. SMD Capacitor in High-Frequency Circuit Experiment
- 85. Axial Capacitor in Power Filtering Experiment
- 86. Variable Capacitor in Tunable Circuits Experiment
- 87. Ceramic Disc Capacitor in RF Circuits Experiment
- 88. Silver Mica Capacitor for High Stability Experiment
- 89. Glass Capacitor in High-Voltage Circuits Experiment
- 90. Inductive Coil in RF Circuit Experiment
- 91. Ferrite Core for Inductor Design Experiment
- 92. Balun Transformer for Impedance Matching Experiment
- 93. Ceramic Multilayer Capacitor in Signal Filtering Experiment
- 94. Transformer in Step-Up/Step-Down Voltage Experiment
- 95. Current Transformer for Current Measurement Experiment
- 96. Electromagnetic Relay in Circuit Switching Experiment
- 97. Reed Switch for Magnetic Field Sensing Experiment
- 98. Hall Effect Sensor in Current Detection Experiment
- 99. Inductive Load in Motor Control Experiment
- 100. Toroidal Core for EMI Suppression Experiment